Herpes Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention: What You Need to Know
Herpes is a common viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding herpes symptoms, treatment, and prevention is crucial for managing the condition and reducing its impact on your life. This blog will delve into the various aspects of herpes, from recognizing its symptoms to exploring effective treatment options and prevention strategies.
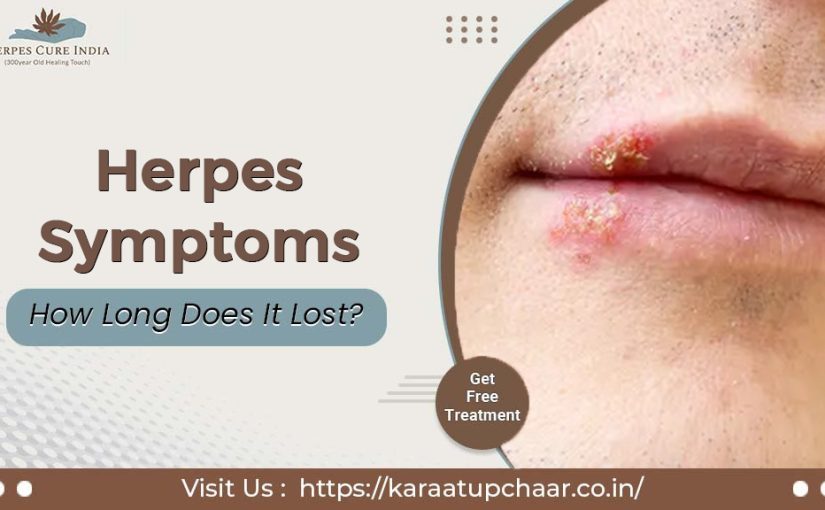
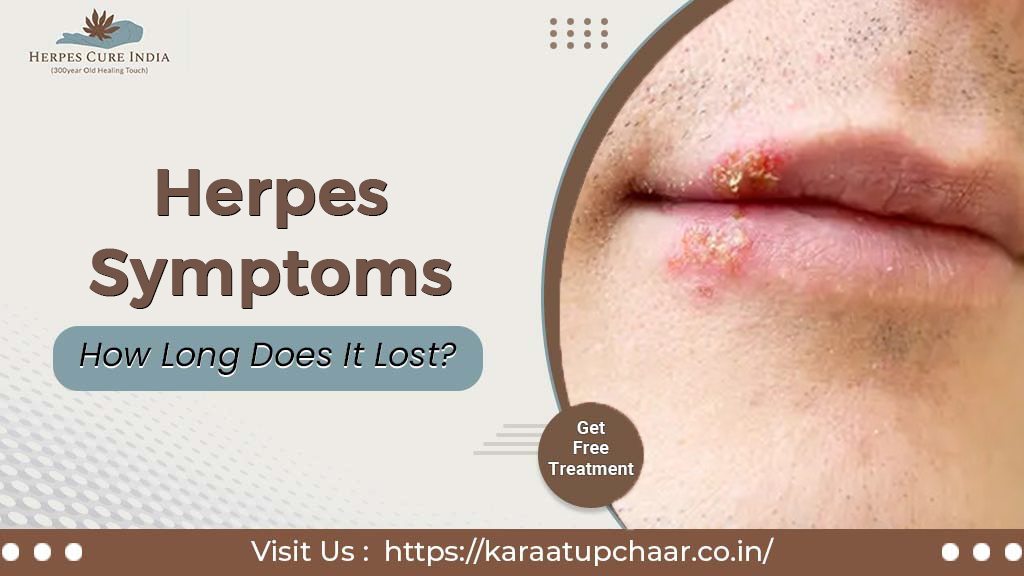
What Are Herpes Symptoms?
Herpes symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) primarily causes two types of infections: HSV-1, which often results in oral herpes, and HSV-2, typically associated with genital herpes.
Common Symptoms
- Painful Sores: The most recognizable symptom is the appearance of painful blisters or sores around the affected area. These can occur on the lips, mouth, genitals, or buttocks.
- Itching and Burning: Before sores appear, many people experience itching or a burning sensation in the affected area.
- Flu-like Symptoms: During the initial outbreak, symptoms may include fever, swollen lymph nodes, and body aches.
Recurring Symptoms
After the initial outbreak, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate, leading to recurrent outbreaks. Symptoms during these episodes are usually milder and shorter in duration.
Herpes Treatment Options
While there is no cure for herpes simplex, effective treatment options can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. Understanding herpes symptoms, treatment, and prevention is essential for anyone diagnosed with the virus.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are the cornerstone of herpes treatment. They help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks and can also lower the risk of transmission to partners. Common antiviral medications include:
- Acyclovir: This medication is often prescribed for treating both oral and genital herpes. It can be taken orally or applied topically.
- Valacyclovir: More convenient than acyclovir, this medication is taken less frequently and is effective in managing outbreaks.
- Famciclovir: This is another option for those who may not respond well to other treatments.
Suppressive Therapy
For individuals who experience frequent outbreaks, suppressive therapy may be recommended. This involves taking antiviral medications daily to prevent outbreaks and reduce the risk of transmission. Many find that this approach significantly improves their quality of life.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing herpes infections is crucial, especially for those at higher risk. Understanding herpes symptoms, treatment, and prevention can help individuals make informed choices about their health.
Safe Sexual Practices
- Condom Use: Using condoms can significantly reduce the risk of transmission during sexual activity. However, it’s important to note that condoms do not provide complete protection, as the virus can be present in areas not covered by the condom.
- Avoiding Sexual Contact During Outbreaks: It is essential to refrain from sexual activity when sores are present to prevent spreading the virus to partners.
- Open Communication: Discussing herpes status with sexual partners can help manage expectations and reduce the risk of transmission.
Lifestyle Choices
Making healthy lifestyle choices can also help reduce the frequency of outbreaks. Consider the following tips:
- Manage Stress: Stress is a common trigger for outbreaks. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise can be beneficial.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support the immune system and may help prevent outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Herpes Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
1. What are the primary herpes symptoms I should look for?
The primary herpes symptoms include painful sores or blisters in the affected area, itching or burning sensations, and flu-like symptoms during the initial outbreak.
2. Is there a cure for herpes?
Currently, there is no cure for herpes. However, antiviral medications can effectively manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
3. How can I prevent the spread of herpes to my partner?
To prevent the spread of herpes, use condoms during sexual activity, avoid sexual contact during herpes outbreaks, and maintain open communication with your partner about your herpes status.
Conclusion
Understanding herpes symptoms, treatment, and prevention is vital for anyone affected by this condition. While there is no cure, effective management strategies and lifestyle changes can help individuals lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the impact of the virus. If you suspect you have herpes or experience symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
Is There a Treatment for Genital Herpes? Understanding Your Options
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the available treatments can help those affected manage their symptoms effectively and lead fulfilling lives. This blog will delve into the treatments for genital herpes, their effectiveness, and some additional tips for management.
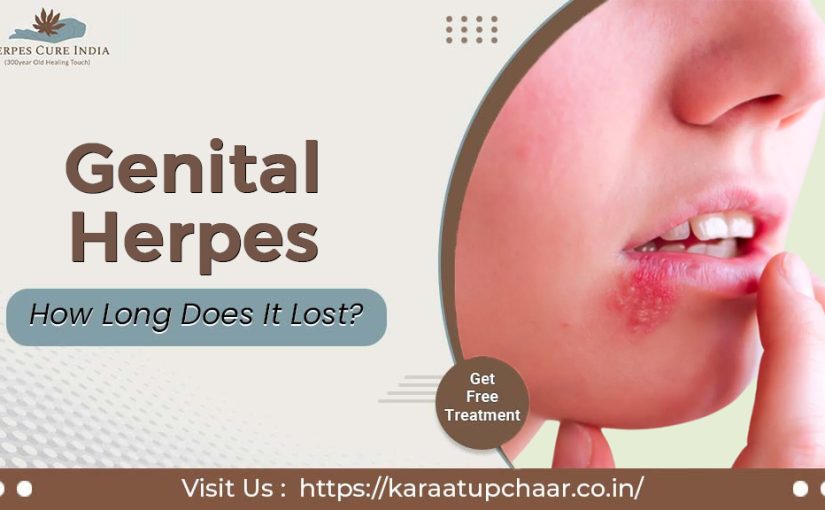
What is Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is primarily caused by two types of herpes simplex viruses: HSV-1 and HSV-2. While HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, it can also result in genital infections. HSV-2 is the most common cause of genital herpes.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
Symptoms may vary between individuals, but common signs include:
- Painful Blisters or Sores: These often appear on the genitals, buttocks, or thighs.
- Itching and Discomfort: A tingling or itching sensation may occur before sores appear.
- Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, swollen lymph nodes, and body aches may accompany initial outbreaks.
The Nature of the Virus
Once contracted, the virus remains in the body for life. It can lay dormant in nerve cells and reactivate, leading to recurrent outbreaks triggered by stress, illness, or other factors.
Is There a Treatment for Genital Herpes?
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are the cornerstone of treatment of genital herpes simplex virus. They work by inhibiting the replication of the virus, thus reducing the severity and duration of symptoms.
Common Antiviral Medications
- Acyclovir: This is the most widely prescribed antiviral for genital herpes. It can be taken orally or applied topically.
- Valacyclovir: A prodrug of acyclovir, valacyclovir is more bioavailable, meaning it requires fewer doses, making it more convenient for patients.
- Famciclovir: This medication is also effective and can be used as an alternative for those who may not respond well to the others.
These medications are typically most effective when taken at the first sign of an outbreak.
Suppressive Therapy
For individuals who experience frequent outbreaks (more than six per year), healthcare providers often recommend suppressive therapy. This involves taking antiviral medications daily to prevent outbreaks and reduce the risk of transmission to partners.
- Benefits of Suppressive Therapy:
- Reduces the frequency of outbreaks.
- Lowers the risk of transmitting the virus to sexual partners.
- Provides peace of mind for those living with the condition.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
While antiviral medications are crucial, many individuals seek complementary approaches to manage symptoms. Here are some popular home remedies and lifestyle changes:
- Keeping the Area Clean and Dry: Regular washing with mild soap and water can help prevent irritation. Keeping the area dry is also essential.
- Wearing Loose Clothing: This helps avoid friction and irritation during outbreaks.
- Stress Management: Since stress is a common trigger for outbreaks, practices such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise can be beneficial.
- Diet and Hydration: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall health and potentially reduce outbreaks.
The Role of Emotional Support
Living with genital herpes can take an emotional toll. Support groups, therapy, or open communication with partners can help individuals cope better and reduce feelings of isolation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can genital herpes be completely cured?
Currently, there is no cure for genital herpes. However, antiviral treatments can help manage symptoms and significantly reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
2. How can I prevent the transmission of genital herpes?
Using condoms and practicing safe sex are crucial in reducing the risk of transmission. Additionally, avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks and discussing the condition openly with partners can help prevent spread.
3. Are there any natural remedies for genital herpes?
While some individuals find relief with natural remedies like aloe vera, coconut oil, or essential oils, these should not replace antiviral herpes medication treatments. Always consult a healthcare provider for the best treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
The question “Is there a treatment for genital herpes?” can be daunting, but understanding the options available can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. With antiviral medications, suppressive therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support, those affected can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their symptoms. If you suspect you have genital herpes or are experiencing symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options.

The two types of herpes simplex virus are HSV-1 and HSV-2 (HSV). Although HSV-1 may also cause genital herpes, it is more often transmitted via direct oral contact, resulting in oral herpes (with cold sore symptoms). Genital herpes is an STD caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2).
According to the reports of the WHO (World Health Organization):
- More than two-thirds (67%) of the world’s population is under the age of 50, and 3.7 billion of them have HSV-1 infection.
- An estimated 491 million people worldwide, or 13%, are infected with HSV-2 and are 15–49 years old.
Herpes symptoms include painful blisters or ulcers that may recur over time. However, the vast majority of HSV infections cause no noticeable signs or symptoms at all. People with HSV-2 infection are more likely to get HIV and pass it on to others.
WHAT CAUSES HERPES?
When one of the herpes simplex viruses enters the body via a cut or scrape and moves through the nerves, it causes herpes. When this virus becomes active, it may cause sores to appear on the skin.
Herpes viruses can spread when they touch open wounds or cuts in the skin, or when they get into the mouth, vagina, penis, or anus.
Cold sores are a common symptom of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infections, which often affect the mouth and lips. Type 1 herpes may be spread by the following means or methods:
- Through intimate actions,
- Kissing and oral sex
- Cuddling
- Through the reuse of an infected person’s objects
- Use of towels
- Use of a toothbrush
- Eating the remaining food, i.e., food eaten by an infected person
Blisters caused by herpes simplex virus 2 may appear anywhere on the body, including the mouth, genitalia (vagina, vulva, cervix), penis, scrotum (balls), butt, and anus. Sexual contact is the transmission route for herpes type 2.
- Intercourse
- Oral sex
- sexually analytic
- Sexual contact between the sexes
- Transmission of herpes by exposure to contaminated sperm or cervical secretions
- Sexual contact with a person who is herpes-positive
ASYMPTOMATIC INFECTIOUS INDIVIDUALS
Even though herpes is most contagious when open sores called ulcers are open or oozing, it can spread even when there are no visible sores and the skin is still healthy. This is called asymptomatic shedding. In other words, the virus is there and can spread even if there are no visible signs of it.
Herpes is always contagious, even when there are no symptoms because there is no way to tell if the virus is shedding when there no symptoms. They risk reinfection if they touch a sore and then scratch or rub another area of skin on their body.
After giving birth vaginally, women infected with HSV-2 may transmit the virus to their infants. This kind of transmission is more probable if the mother recently contracted the virus.
WAYS THROUGH WHICH THE DORMANT VIRUS GETS TRIGGERED
Many people who are infected with the herpes virus at an early stage, or who are asymptomatic, have a high chance that the herpes virus will remain latent for long periods of time. An outbreak (or assault) could be triggered by any of the following circumstances:
- An infection, disease, injury, or physical stress.
- Persistent emotional stress or distress for more than a week
- Illness in general (from mild illnesses to serious conditions)
- Immuno suppression as a consequence of having AIDS
- Using medications such as chemotherapy or steroids.
- Fatigue.
- Both sexual activity and trauma to the affected area are considered risk factors.
- Menstruation
HOW DO HERPES OUTBREAKS HAPPEN?
The HSV virus is responsible for initiating the process of viral replication after entering the nucleus of an infected human cell. Even if any of your cells have been infected, it is quite unlikely that you will have any symptoms at this stage.
During the first stage of infection, the virus travels through nerve cells to places known as ganglia, which are nerve-branching areas. The virus will continue to stay dormant and dormant on that site; it will neither reproduce nor show any indications of its existence during this time.
Sometimes the dormant virus will become active again (through the means that have been mentioned above), which will start the process of replication all over again. When this takes place, the virus makes its way back to the surface of the skin via the nerve. Blistering results from the death of a significant number of the infected skin cells brought about by this. When these blisters break open, they turn into sores or ulcers that are known as cold sores or genital herpes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Herpes
Are herpes and shingles the same?
Herpes and shingles are not the same, though they are both caused by viruses in the herpesvirus family. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes oral and genital herpes, characterized by blisters and sores. Shingles, or herpes zoster, is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox. Shingles results in a painful rash and blisters, usually on one side of the body. While both conditions involve painful skin eruptions, they are distinct diseases with different causes and patterns of transmission. Treatment for both typically involves antiviral medications to manage symptoms.

If you are looking for the best Ayurvedic treatment for herpes zoster, you have come to the right place. Herpes zoster, We are Offering free Ayurvedic Herble Oils, and cream. That is homemade from Ayurvedic medicines using the traditional Ayurveda method to treat herpes. Commonly known as shingles, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. It is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. The virus remains dormant in the body’s nerve tissues after a person has had chickenpox and can reactivate later in life.
Herpes zoster is a viral infection caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nervous system and can reactivate years later, causing Herpes Shingles. The condition is characterized by painful rashes and blisters that can last for weeks or even months.
Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine, offers a holistic approach to healing that focuses on balancing the body, mind, and spirit. Our Free Ayurvedic Herpes Treatments in India are safe, and effective, and can help alleviate symptoms, boost immunity, and promote overall well-being.
So, let’s dive into the Best Ayurvedic Treatment For Herpes Zoster.
CAUSES OF HERPES ZOSTER
Before we delve into the Best Ayurvedic Treatment For Herpes Zoster, let’s first understand the causes of this condition. As mentioned earlier, Herpes Zoster is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox, the varicella-zoster virus. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nervous system and can reactivate later in life, causing Herpes Zoster.
Factors that can trigger the reactivation of the virus include stress, weakened immunity, aging, and certain medications.
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
The symptoms of Herpes Zoster can vary from person to person but typically include:
- Painful rashes and blisters on one side of the body
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Itching
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to light
Best Ayurvedic Treatment For Herpes Zoster
Ayurveda offers a variety of herbs, therapies, and lifestyle changes that can effectively alleviate the symptoms of Herpes Zoster and promote overall well-being. Here are some of the Best Ayurvedic Herpes Treatment in India:
- Tulsi (Holy Basil): Tulsi is a potent antiviral and immunomodulatory herb that can help boost the immune system and fight the herpes zoster virus. You can consume tulsi leaves by boiling them in water or by making a tea.
- Neem (Indian Lilac): Neem has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties that can help relieve the pain and itching associated with herpes zoster. You can apply neem oil on the affected area or make a paste with neem leaves and apply it on the rash.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe the skin and reduce the pain and inflammation associated with herpes zoster. You can apply aloe vera gel on the affected area or drink aloe vera juice to boost your immunity.
- Turmeric: Turmeric is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant herb that can help reduce the inflammation and pain associated with herpes zoster. You can consume turmeric powder by mixing it with warm milk or water.
- Ashwagandha (Indian ginseng): Ashwagandha is a potent adaptogenic herb that can help boost your immunity and reduce stress. You can consume ashwagandha powder or extract in the form of capsules or tablets.
We always recommend taking a consult with our qualified Ayurvedic practitioner. Get a Free Herpes Cure in India, we offer a homemade Ayurvedic herbal oil. We manufacture Oils, a cream which is made from Ayurvedic medicines using the traditional Ayurveda method to treat Herpes.
Our Oil’s are free of charge, no cost, Services available all over India
Call Us At- 9954064243, 9435115363, or 9435015362.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the Ayurvedic treatment for Herpes Zoster?
Ayurvedic treatment for Herpes Zoster includes a holistic approach that focuses on balancing the body, mind, and spirit. It includes the use of various herbs, therapies, and lifestyle changes to alleviate the symptoms of this condition and promote overall well-being.
Q2: Is Ayurvedic treatment safe for Herpes Zoster?
Yes, Ayurvedic treatment is generally safe for Herpes Zoster. Ayurvedic herbs and therapies are natural and have been used for centuries to treat various health conditions, including Herpes Zoster. However, it is always recommended to consult a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner before starting any treatment.
Q3: How long does Ayurvedic treatment take to show results for Herpes Zoster?
The duration of Ayurvedic treatment for Herpes Zoster depends on various factors, such as the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and their adherence to the treatment plan. Generally, Ayurvedic treatments take time to show results as they focus on treating the root cause of the condition.
Q4: Can Ayurvedic treatment cure Herpes Zoster completely?
There is no known cure for Herpes Zoster, but Ayurvedic treatment can effectively alleviate the symptoms and prevent the recurrence of the condition. Ayurvedic herbs and therapies can boost immunity, reduce inflammation and pain, and promote overall well-being, which can help manage the symptoms of Herpes Zoster.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Herpes
Can herpes be treated?
Yes, herpes can be treated, although it cannot be cured. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, reducing the frequency of outbreaks, and lowering the risk of transmission. Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, are commonly prescribed to help control the virus. These medications can speed up the healing of sores, reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, and decrease the likelihood of future outbreaks. Ayurvedic treatments for herpes include using herbs like neem, turmeric, and aloe vera to soothe the skin and boost immunity. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding direct contact during outbreaks, and using condoms can help manage and prevent the spread of herpes. While treatment helps manage the condition, the virus remains in the body and can reactivate.
Are herpes common?
Yes, herpes is very common. The two main types, HSV-1 and HSV-2, are widespread globally. HSV-1, which typically causes oral herpes, affects about 67% of the world’s population under the age of 50, according to the World Health Organization. It often results in cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth.
HSV-2, which primarily causes genital herpes, affects around 11% of the global population aged 15-49. It is transmitted through sexual contact and results in sores in the genital or anal area.
Due to the high prevalence, many people may have herpes without experiencing noticeable symptoms, contributing to its widespread nature.

Herpes virus infection is caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster (VZV) dormant in the sensory ganglia following primary infection. This is a painful blister or rash on the affected area as the virus travels along sensory nerve fibers. The annual incidence of herpes virus is similar in Asia Pacific, North America, and Europe at 3 to 5 cases per 1000 person-years (PY). The incidence of herpes viruses increases markedly with age and Immunosuppression, affecting more than 50% of people over the age of 85.
Diabetic patients are susceptible to herpes virus infection due to decreased cell-mediated immunity (CMI) during this process and the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is generally recognized as a prothrombotic disease associated with altered innate or adaptive immunity and endothelial dysfunction secondary to inflammation. Therefore, diabetes mellitus with chronic comorbidities or associated vascular complications is considered a major preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Diabetic patients are two to four times more likely to develop cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease than non-diabetic patients. Patients are at increased risk of developing the herpes virus if they have two or more comorbidities. On the other hand, herpes zoster was an independent risk factor for VZV vascular lesions such as stroke, transient ischemic attack, and myocardial infarction. However, few studies have examined the association between shingles risk and diabetes-related micro vascular disease in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
The aim of this study was to determine whether the risk of herpes zoster in diabetic patients increases with the co-occurrence of coronary artery disease or with other associated microvascular diseases. In addition, we assessed the effect of anti-diabetic drugs on the risk of herpes viruses in these patients using data from a national database in Taiwan.
HERPES TRIGGERS DIABETES PATIENTS
A common herpes virus can trigger diabetes in people with diabetes. People infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) may have a 50% increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Previous research has shown that hepatitis C virus infection is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. However, it is also possible that infection with other viruses can make people more susceptible to the disease.
The current study tested HSV-1 infection in 206 participants with type 2 diabetes and a control group of 1,360 participants without diabetes. All participants were negative for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, the researchers found. The findings showed that 46 percent of the diabetic patients were infected with HSV-1, compared with 36 percent of the control group. In a Diabetes Care (February 2005) report, researchers showed that people with diabetes accounted for 16 percent of the HSV-1-infected population, but only 11 percent of them were free of the virus.
WHY DIABETES MAKES IT EASY TO CONTRACT HERPES
Most people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes have a weakened immune system, making it easier to get infections and thus harder to fight off. Because of this, people with diabetes are more susceptible to viral infections, including herpes simplex virus (HSV). HSV is one of the most common and easily contracted STDs, and people with diabetes can contract HSV if they are not careful with someone who is already infected.
Herpes and Type 1 Diabetes The herpes virus remains in the body’s nerve cells indefinitely, regardless of whether the person has frequent or infrequent attacks. While these can be triggered by lifestyle changes (eg, stress, menstruation), having a compromised immune system in diabetics puts them at constant risk of flare-ups.
How to Prevent Herpes in terms of Diabetic Patients?
The best protection against HSV in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes is prevention. While a weakened immune system can make it easier to catch the virus, there are steps you can take to avoid it. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends avoiding specific contact with infected people as a best precaution, including:
• Have vaginal, anal, or oral
• Kiss
• Shared drinks or cutlery
If you have type 1 or 2 diabetes and are concerned about your risk of contracting the herpes virus, visit https://herpescure.in Healthcare professionals are available 365 days a year to educate you about the risks and testing for STDs. Stop by today!

Cure for herpes simplex virus with herpes cure website. Herpes zoster sometimes referred to as shingles, is a common nerve illness brought on by a virus that presents as a painful blister rash anywhere on the body. Even after the rash has healed, the pain may linger for months. The virus is the same as the one that causes chickenpox. Throughout a person’s lifetime, the virus stays latent in the body and may reawaken years or even decades later to produce a zoster.
WHO IS AT RISK OF DEVELOPING HERPES SHINGLES?
It is more likely that someone who has had chickenpox would acquire shingles.
Due to compromised defenses (such as people with cancer, HIV, organ transplant recipients, or those receiving chemotherapy).
- Who is in distressed condition?
- Who has reached or is above the age of 50?
- People who are ill
- Who has experienced trauma?
Infected individuals will not develop symptoms until the chickenpox virus has completely replicated within their bodies. The virus stays put in the dorsal root ganglion of your spinal nerve. The vast majority of the population has no idea the virus even exists in their body. Stress is a common precipitating factor in herpes virus resurgence; Take a the best Ayurvedic Treatment for herpes cure, by nature herbal oils.
SYMPTOMS
Shingles are characterized by a red, itchy rash, as the name suggests. Shingles often affect just one side of the body or one side of the face at a time. Even if you haven’t seen any signs of the rash yet, itching, burning, or tingling in the areas where it will appear may irritate you.
The effects of the sickness on the nervous system might last months or even years. Long-term nerve soreness becomes more common as you get older. There have been reports of searing, throbbing, aching, or stinging nerve discomfort.
Shingles may cause conjunctivitis of the eyes.
One of the first signs of herpes simplex virus is:
- Fever
- Chill bumps
- Worn out.
- Sensitivity towards light
- I went to the doctor because I was experiencing stomach pains.
- The skin might itch or feel like it’s burning in one area alone.
- The skin may have a little, raised rash;
- The affected area of the skin will be darkened
- Fluid-filled sores that eventually scab over.
PREVENTION IS BETTER THAN CURE. GO FOR VACCINATION
You can cure for herpes simplex virus with a simple and effective vaccination. Getting vaccinated is the most effective way to reduce the chance of developing shingles or experiencing long-term pain if one does get shingles. Vaccination against zoster is recommended for all healthy adults 50 and older, as well as those 19 and older with compromised immunity owing to disease or treatment. Even if a person has already had chickenpox, the infection might recur. Those who have already had chickenpox are still able to get a vaccine to prevent future outbreaks. Although there is no specific time restriction for receiving the varicella vaccination after having chickenpox, you should often wait until the outbreak has subsided before receiving the vaccine. The vaccination regimen should be discussed with a medical professional.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Herpes
Can herpes go away?
Herpes, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), does not go away permanently because the virus remains in the body for life. After the initial infection, the virus stays dormant in nerve cells and can reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks. These outbreaks might decrease in frequency and severity over time. Antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks but do not eradicate the virus. While herpes cannot be completely cured or eliminated from the body, many people experience long periods without symptoms and can manage the condition effectively.

Best Ayurvedic Treatment For Herpes Zoster By Nature Herbal Remedies
If you are looking for the best Ayurvedic treatment for herpes zoster, you have come to the right place. Herpes zoster, commonly known as herpes shingles, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. It is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. The virus remains dormant in the body’s nerve tissues after a person has had chickenpox and can reactivate later in life. We are offering free Ayurvedic herbal oils and cream, which are homemade from best Ayurvedic medicines for herpes using the traditional Ayurveda method to treat herpes.
Causes of Herpes Zoster
Before we delve into the best Ayurvedic treatment for herpes zoster, let’s first understand the causes of this condition. Herpes Zoster is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nervous system and can reactivate later in life, causing Herpes Zoster. Factors that can trigger the reactivation of the virus include stress, weakened immunity, aging, and certain medications.
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
The symptoms of Herpes Zoster can vary from person to person but typically include:
- Painful rashes and blisters on one side of the body
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Itching
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to light
Best Ayurvedic Treatment for Herpes Zoster
Ayurveda offers a variety of herbs, therapies, and lifestyle changes that can effectively alleviate the symptoms of Herpes Zoster and promote overall well-being. Here are some of the best Ayurvedic treatments for herpes in India:
Tulsi (Holy Basil): Tulsi is a potent antiviral and immunomodulatory herb that can help boost the immune system and fight the herpes zoster virus. You can consume tulsi leaves by boiling them in water or by making a tea.
Neem (Indian Lilac): Neem has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties that can help relieve the pain and itching associated with herpes zoster. You can apply neem oil on the affected area or make a paste with neem leaves and apply it to the rash.
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe the skin and reduce the pain and inflammation associated with herpes zoster. You can apply aloe vera gel on the affected area or drink aloe vera juice to boost your immunity.
Turmeric: Turmeric is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant herb that can help reduce the inflammation and pain associated with herpes zoster. You can consume turmeric powder by mixing it with warm milk or water.
Ashwagandha (Indian ginseng): Ashwagandha is a potent adaptogenic herb that can help boost your immunity and reduce stress. You can consume ashwagandha powder or extract in the form of capsules or tablets.
We always recommend consulting with our qualified Ayurvedic practitioner. Get a free herpes cure in India; we offer a homemade Ayurvedic herbal oil. We manufacture oils and creams made from best Ayurvedic medicines for herpes using the traditional Ayurveda method to treat herpes.
Our oils are free of charge, with no cost, and services are available all over India.
Call Us At- 9954064243, 9435115363, or 9435015362.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Ayurvedic Treatment for Herpes
Q1: What is the Ayurvedic treatment for Herpes Zoster?
Ayurvedic treatment for Herpes Zoster includes a holistic approach that focuses on balancing the body, mind, and spirit. It includes the use of various herbs, therapies, and lifestyle changes to alleviate the symptoms of this condition and promote overall well-being.
Q2: Is Ayurvedic treatment safe for Herpes Zoster?
Yes, Ayurvedic treatment is generally safe for Herpes Zoster. Ayurvedic herbs and therapies are natural and have been used for centuries to treat various health conditions, including Herpes Zoster. However, it is always recommended to consult a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner before starting any treatment.
Q3: How long does Ayurvedic treatment take to show results for Herpes Zoster?
The duration of Ayurvedic treatment for Herpes Zoster depends on various factors, such as the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and their adherence to the treatment plan. Generally, Ayurvedic treatments take time to show results as they focus on treating the root cause of the condition.
Q4: Can Ayurvedic treatment cure Herpes Zoster completely?
There is no known cure for Herpes Zoster, but Ayurvedic treatment can effectively alleviate the symptoms and prevent the recurrence of the condition. Ayurvedic herbs and therapies can boost immunity, reduce inflammation and pain, and promote overall well-being, which can help manage the symptoms of Herpes Zoster.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Herpes
Can herpes be treated?
Yes, herpes can be treated, although it cannot be cured. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, reducing the frequency of outbreaks, and lowering the risk of transmission. Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, are commonly prescribed to help control the virus. These medications can speed up the healing of sores, reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, and decrease the likelihood of future outbreaks. Ayurvedic treatments for herpes include using herbs like neem, turmeric, and aloe vera to soothe the skin and boost immunity. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding direct contact during outbreaks, and using condoms can help manage and prevent the spread of herpes. While treatment helps manage the condition, the virus remains in the body and can reactivate.
Are herpes common?
Yes, herpes is very common. The two main types, HSV-1 and HSV-2, are widespread globally. HSV-1, which typically causes oral herpes, affects about 67% of the world’s population under the age of 50, according to the World Health Organization. It often results in cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth.
HSV-2, which primarily causes genital herpes, affects around 11% of the global population aged 15-49. It is transmitted through sexual contact and results in sores in the genital or anal area.
Due to the high prevalence, many people may have herpes without experiencing noticeable symptoms, contributing to its widespread nature.

Herpes Virus Infection Increases the Risk for Diabetes Patients
Herpes virus infection is caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) dormant in the sensory ganglia following primary infection. This results in a painful blister or rash on the affected area as the virus travels along sensory nerve fibers. The annual incidence of herpes virus is similar in the Asia Pacific, North America, and Europe, at 3 to 5 cases per 1000 person-years (PY). The incidence of herpes viruses increases markedly with age and immunosuppression, affecting more than 50% of people over the age of 85.
Diabetic patients are susceptible to herpes virus infection due to decreased cell-mediated immunity (CMI) during this process and the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is generally recognized as a prothrombotic disease associated with altered innate or adaptive immunity and endothelial dysfunction secondary to inflammation. Therefore, diabetes mellitus with chronic comorbidities or associated vascular complications is considered a major preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Diabetic patients are two to four times more likely to develop cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease than non-diabetic patients. Patients are at increased risk of developing the herpes virus if they have two or more comorbidities. On the other hand, herpes zoster is an independent risk factor for VZV vascular lesions such as stroke, transient ischemic attack, and myocardial infarction. However, few studies have examined the association between shingles risk and diabetes-related microvascular disease in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
The aim of this study was to determine whether the risk of herpes zoster in diabetic patients increases with the co-occurrence of coronary artery disease or with other associated microvascular diseases. In addition, we assessed the effect of anti-diabetic drugs on the risk of herpes viruses in these patients using data from a national database in Taiwan.
Herpes Virus Infection Triggers Diabetes Patients
A common herpes virus can trigger diabetes in people with diabetes. People infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) may have a 50% increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Previous research has shown that hepatitis C virus infection is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. However, it is also possible that infection with other viruses can make people more susceptible to the disease.
The current study tested HSV-1 infection in 206 participants with type 2 diabetes and a control group of 1,360 participants without diabetes. All participants were negative for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, the researchers found. The findings showed that 46 percent of the diabetic patients were infected with HSV-1, compared with 36 percent of the control group. In a Diabetes Care (February 2005) report, researchers showed that people with diabetes accounted for 16 percent of the HSV-1-infected population, but only 11 percent of the non-diabetic group were free of the virus.
Why Diabetes Makes It Easy to Contract Herpes Virus Infection
Most people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes have a weakened immune system, making it easier to get infections and harder to fight them off. Because of this, people with diabetes are more susceptible to viral infections, including herpes simplex virus (HSV). HSV is one of the most common and easily contracted STDs, and people with diabetes can contract HSV if they are not careful with someone who is already infected.
Herpes and Type 1 Diabetes
The herpes virus remains in the body’s nerve cells indefinitely, regardless of whether the person has frequent or infrequent attacks. While these can be triggered by lifestyle changes (e.g., stress, menstruation), having a compromised immune system in diabetics puts them at constant risk of flare-ups.
How to Prevent Herpes Virus Infection in Diabetic Patients
The best protection against HSV in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes is prevention. While a weakened immune system can make it easier to catch the virus, there are steps you can take to avoid it. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends avoiding specific contact with infected people as a best precaution, including:
– Having vaginal, anal, or oral sex
– Kissing
– Sharing drinks or cutlery
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and are concerned about your risk of contracting the herpes virus, visit https://karaatupchaar.co.in/. Healthcare professionals are available 365 days a year to educate you about the risks and testing for STDs. Stop by today!

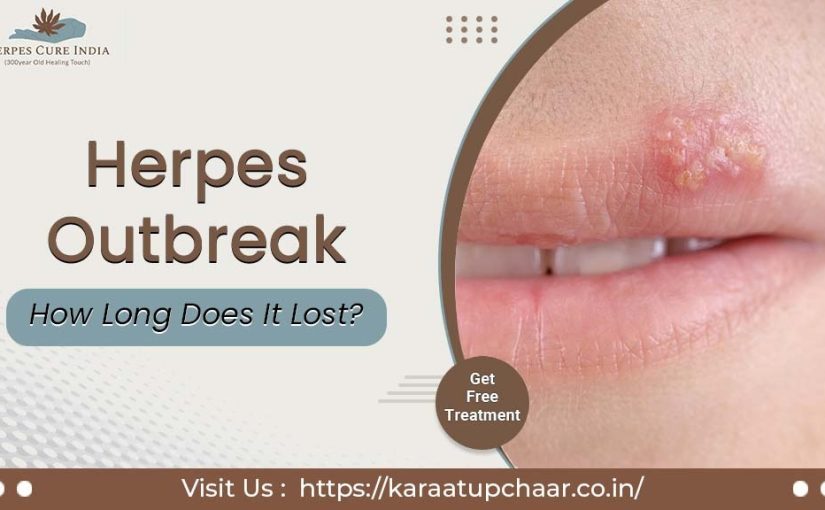
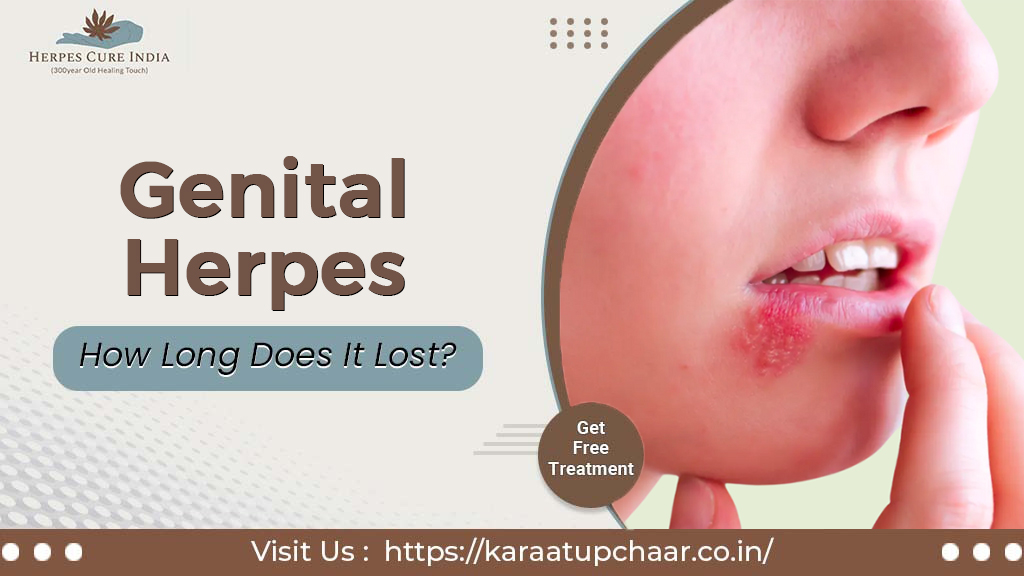
When Get Herpes Outbreak?
Herpes outbreaks can become at any time once a person is infected with the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is a common sexually transmitted infection. The initial Herpes outbreak typically occurs within two weeks to a month of the initial infection, but sometimes herpes outbreaks may happen with varying frequency and severity. Outbreaks can be become by various factors such as stress, illness, fatigue, hormonal changes, and certain unused medications. It’s important to note that sometimes herpes can still be transmitted even when there are no visible symptoms, so practicing safe sex and disclosing your status to sexual partners is crucial in preventing its spread.
Use the following Points to protect from Herpes Outbreak
To protect yourself from a herpes outbreak, you can take the following steps:
1, Avoid close contact with someone who has an active herpes outbreak.
2, Do always have safe sex, including using condoms or dental dams during oral sex.
3, Avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, or utensils with someone who has an active herpes outbreak.
4, Manage stress levels as high levels of stress can create herpes outbreaks.
5, Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet. Take antiviral medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
How do Stay Safe from Herpes Outbreaks During Pregnancy?
If you have genital herpes and are pregnant, it’s important to talk to your healthcare, and know how to reduce the risk of Genital (HSV) virus in Pregnancy’s women and her babies. Here are some tips to help stay safe from herpes outbreaks.
- Take antiviral medication: Your healthcare provider may prescribe antiviral medication to help prevent or reduce the severity of Herpes outbreaks during pregnancy.
- Do Practice Alway good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and keep the genital area clean and dry to reduce the risk of infection for away herpes outbreak.
- Avoid sexual contact during outbreaks: If you or your partner has an active Herpes outbreak of herpes, avoid sexual contact until the outbreak has healed.
- Use condoms: Using condoms during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of transmitting herpes Outbreak to your partner or the baby.
- Consider a C-section: If you have active herpes lesions at the time of delivery, your healthcare provider may recommend a cesarean section to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to your baby during delivery.
When herpes viruses come into contact with open sores or cuts on the skin, or when they enter the mouth, vagina, penis, or anus, they may spread. And the stages through which a person has to go are mentioned below:
Initial Herpes Outbreak Stage
Often, the initial outbreak of herpes is the most severe, and women typically have more severe symptoms than males. The initial outbreak normally occurs a few weeks after contracting the virus. The majority of symptoms often disappear within two to three weeks.
Multiple genital blisters are indicative of an initial (or main) bout of genital herpes outbreaks. According to gender, the most often afflicted areas are the vagina, vulva, buttocks, anus, and thighs for women, and the penis, scrotum, anus, buttocks, and thighs for males. Typical symptoms and indicators include blisters that progress into painful ulcers. On the penis or outer labia, blisters may harden and vanish. Up to five to seven days after the appearance of the first set of lesions, more lesions may emerge.
In addition, painful urination, sore, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, and flu-like symptoms such as joint pain, fever, and headaches may be present. Some individuals may develop headaches, nausea, and vomiting, in addition to difficulty urinating. When the herpes outbreak simplex virus affects the nervous system, certain symptoms manifest. Proctitis (rectum or anus inflammation) can cause urination discomfort in some people. This problem is more prevalent among males who engage in sexual activity with others than among other patients.
Latent Stage: Following the first Herpes outbreak, the virus migrates to a clump of nerves near the base of the spine, where it finally stays dormant. This occurs during the latent stage. The stage has no symptoms.
Recurring episodes of the outbreak: Many people experience recurrent bouts of genital herpes, which occurs when the virus travels to the skin’s surface through nerves and causes an ulcer flare-up. The initial herpes outbreak was often much worse than these repeating episodes.
Ulcers may develop at new sites or return to the site of the original outbreak. Lesions may occur in areas where there was no direct touch, such as the anus region, where there was no anal intercourse.
The possibility of a herpes outbreak: many people with genital herpes, particularly those infected with HSV type 2, experience frequent relapses. Over time, recurrences often become milder and less frequent. A recurrence of the HSV infection a few years after the first infection is also possible. If you did not have symptoms after the first infection, this kind of delayed herpes outbreak may be distressing and cause you to worry about the behavior of your prior or present sexual partner (s).
Causes of Herpes outbreaks: illness, stress, sunlight, and tiredness can all cause herpes outbreaks to happen again and again. In women, an outbreak may be caused by their periods.
Note: Up to fifty percent of people who have a recurring outbreak have symptoms that occur before the formation of ulcers. This is referred to as the prodrome. Some instances of prodromal symptoms include itching, tingling, or discomfort in the buttocks, legs, or hips. Recurrences have a tendency to become less common and less severe once the first year has passed.
If you want to get free herpes treatment from us, then visit our website-
Call Us –
- Trinagar Kamal Agarwal (Hargovind Chahcha) – 9013289821
- FD 46, Pitampura Prachi Agarwal – 9811718621
- Ramprastha, Vaisali, Noida Ravi Agarwal – 9911395464
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Herpes
Can herpes spread?
Yes, herpes can spread from person to person through direct contact with an infected area. The two main types, herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2), are spread through different means. HSV-1, which commonly causes oral herpes, is typically spread through kissing or sharing personal items like utensils or lip balm. HSV-2, which primarily causes genital herpes, spreads through sexual contact. Both types can spread even when symptoms are not present due to asymptomatic shedding of the virus. Preventive measures include using condoms, taking antiviral medications, and avoiding contact during outbreaks.
Can herpes spread through air?
Herpes cannot spread through the air. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) requires direct skin-to-skin contact for transmission. HSV-1, responsible for oral herpes, spreads primarily through activities such as kissing or sharing utensils and personal items. HSV-2, which causes genital herpes, spreads mainly through sexual contact. Both types of herpes are transmitted via direct contact with infected sores, skin, or mucous membranes. The virus does not survive long outside the body, making airborne transmission or spread through casual contact highly unlikely. To prevent herpes transmission, avoid direct contact with sores and practice good hygiene.

Cure for Herpes Simplex: Understanding and Managing the Virus
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a common and often misunderstood infection that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, there are many misconceptions about the virus, its symptoms, and its treatment. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of herpes simplex, its causes, symptoms, and most importantly, the options available for managing and potentially curing the infection.
What is Herpes Simplex?
Herpes simplex virus comes in two forms: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 primarily causes oral herpes, which is characterized by cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth. HSV-2, on the other hand, is typically responsible for genital herpes, which affects the genital and anal areas. However, both types can cause infections in either location.
The virus is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person. This includes kissing, sexual contact, and even sharing items like utensils or lip balm with someone who has an active outbreak.
Symptoms of Herpes Simplex
The symptoms of herpes simplex can vary widely among individuals. Some people may experience severe outbreaks, while others may have mild symptoms or none at all. Common symptoms include:
– Painful blisters or sores on the lips, mouth, genital, or anal areas
– Itching or burning sensations in the affected areas
– Flu-like symptoms such as fever, swollen lymph nodes, and body aches
– Painful urination (in the case of genital herpes)
The initial outbreak is often the most severe, with subsequent recurrences becoming less intense over time. These recurrences are triggered by factors such as stress, illness, or a weakened immune system.
Diagnosis and Testing
If you suspect you have herpes simplex, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can diagnose the infection through a physical examination and by taking a sample from the sore for laboratory testing. Blood tests can also detect HSV antibodies, indicating a past or current infection.
Options for Cure for Herpes Simplex
While there is currently no cure for herpes simplex, several herpes medication treatment options can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. These include:
1. Antiviral Medications:
Antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are commonly prescribed to treat herpes simplex. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus, thereby reducing the severity and duration of outbreaks. They can be taken during an outbreak (episodic treatment) or daily (suppressive therapy) to prevent recurrences.
2. Topical Treatments:
Over-the-counter and prescription creams and ointments can be applied directly to the sores to alleviate pain and promote healing. Examples include docosanol and acyclovir cream.
3. Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage the discomfort associated with herpes sores. Additionally, applying a cold compress to the affected area can provide temporary relief.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage herpes simplex symptoms:
1. Keep the Affected Area Clean and Dry:
Gently wash the area with mild soap and water and pat it dry. Avoid tight-fitting clothing that can irritate the sores.
2. Avoid Triggers:
Identify and avoid triggers that may cause outbreaks, such as stress, illness, and certain foods.
3. Boost Your Immune System:
A healthy immune system can help keep the virus in check. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get plenty of rest.
4. Use Protection:
During sexual activity, use condoms to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to your partner.
The Search for a Cure for Herpes Simplex
The quest for a cure for herpes simplex is ongoing, with researchers exploring various avenues, including vaccines, gene editing, and new antiviral drugs. Some promising developments include:
1. Vaccines:
Several experimental vaccines are in development, aiming to prevent HSV infection or reduce the severity of outbreaks in those already infected.
2. Gene Editing:
CRISPR technology is being investigated as a potential tool to target and remove the herpes virus from infected cells.
3. Novel Antivirals:
New antiviral compounds are being tested for their effectiveness in treatment of herpes simplex, with some showing promising results in early clinical trials.
Prevention and Cure for Herpes Simplex
While there is no surefire way to prevent herpes simplex infection, certain measures can reduce the risk:
– Avoid direct contact with the sores of an infected person.
– Use protection during sexual activity.
– Avoid sharing personal items that may have come into contact with the virus.
Conclusion
Herpes simplex is a manageable condition, and with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, individuals can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. While a cure for herpes simplex remains elusive, ongoing research offers hope for more effective treatments and possibly a future cure. If you suspect you have herpes simplex, consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
For more detailed information and support, visit the [Herpes Cure](https://herpescure.in) website, where healthcare professionals are available to assist you in managing and preventing herpes simplex virus infections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Herpes
Can herpes go away?
Herpes, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), does not go away permanently because the virus remains in the body for life. After the initial infection, the virus stays dormant in nerve cells and can reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks. These outbreaks might decrease in frequency and severity over time. Antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks but do not eradicate the virus. While herpes cannot be completely cured or eliminated from the body, many people experience long periods without symptoms and can manage the condition effectively.